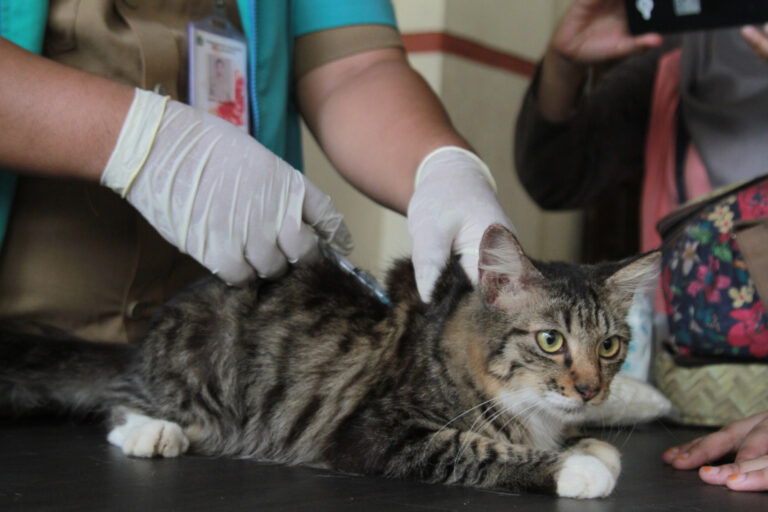
Pengenalan: Mengapa Vaksinasi Itu Penting untuk Hewan Peliharaan? Seperti manusia, hewan peliharaan juga membutuhkan vaksinasi untuk melindungi...
Blog
Pengenalan: Keuangan yang Teratur Adalah Kunci Sukses Bisnis Kecil Bagi pemilik bisnis kecil, salah satu tantangan terbesar...
Pengenalan: Mengapa Kebugaran Tubuh Itu Krusial bagi Atlet? Bagi seorang atlet, kebugaran tubuh bukan hanya sekadar faktor...
Pengenalan: Hewan Peliharaan yang Menjadi Teman Sejati Hewan peliharaan telah menjadi bagian penting dalam kehidupan banyak orang...
“7 Tips Jitu Mencari Properti dengan Harga Terjangkau di Tengah Peningkatan Pasar Properti Indonesia


“7 Tips Jitu Mencari Properti dengan Harga Terjangkau di Tengah Peningkatan Pasar Properti Indonesia
Pendahuluan Harga properti di Indonesia terus mengalami kenaikan signifikan, terutama di kota-kota besar seperti Jakarta, Surabaya, dan...
Fenomena Hoaks Semakin Marak Di era digital saat ini, media sosial telah menjadi sumber utama informasi bagi...
Pemerintah Bergerak, Rakyat Perlu Tahu Tahun 2025 menandai era baru dalam arah kebijakan nasional. Sejumlah langkah strategis...
Pengenalan Kesehatan jangka panjang bergantung pada banyak faktor, dan salah satu faktor yang paling penting adalah pola...
Apa Itu Piala Dunia? Piala Dunia FIFA adalah turnamen sepak bola internasional paling bergengsi yang diselenggarakan oleh...
Pengenalan Gen Z, yang lahir antara tahun 1997 hingga 2012, merupakan generasi pertama yang tumbuh dengan teknologi...
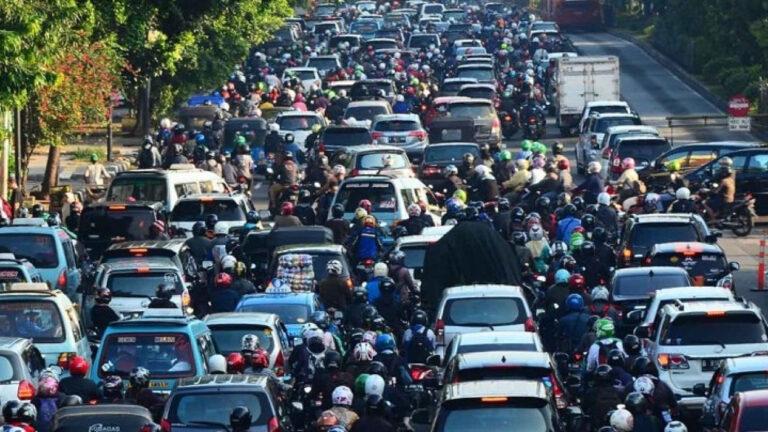
Pengenalan Kemacetan di JakartaJakarta, sebagai ibu kota Indonesia, dikenal dengan kemacetan yang parah. Setiap hari, jutaan orang...
Siapa Itu Gen Z?Gen Z (Generasi Z) adalah kelompok demografis yang lahir antara tahun 1997 dan 2012....
Apa Itu Liga BRI Indonesia?Liga BRI Indonesia adalah kompetisi sepak bola profesional teratas di Indonesia. Sebelumnya dikenal...
Busana muslimah telah mengalami evolusi signifikan seiring dengan perkembangan zaman. Salah satu elemen penting dalam busana muslimah...
Dalam dunia kedokteran modern, tes medis memainkan peran yang sangat penting dalam diagnosis, pengobatan, dan pencegahan penyakit....
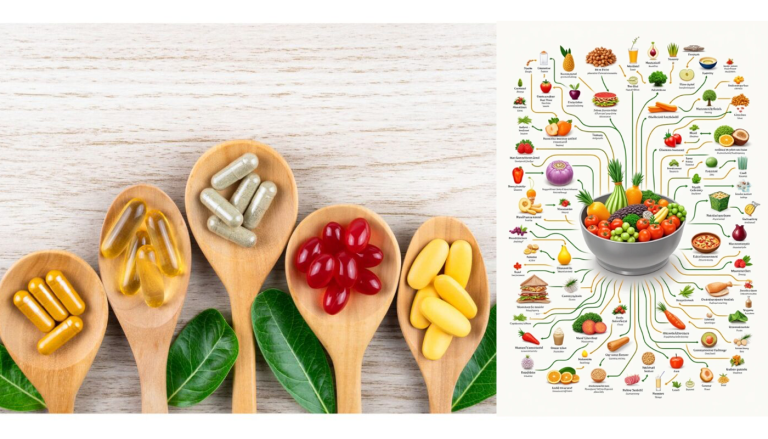
Di tengah gaya hidup modern yang serba cepat, banyak orang kesulitan memenuhi kebutuhan gizi seimbang hanya dari...
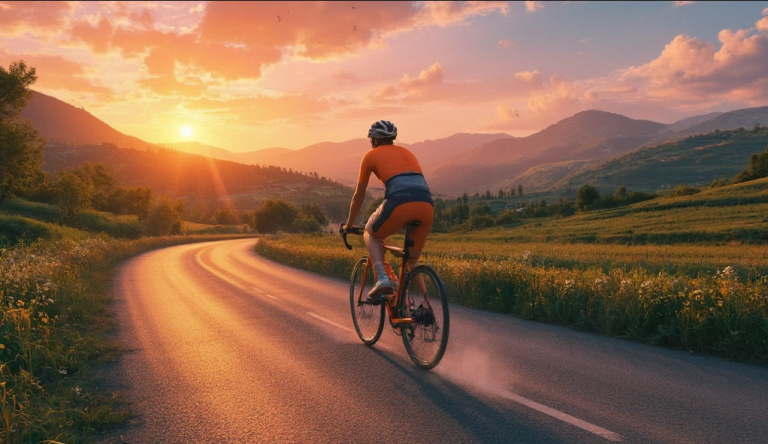
Di tengah kesibukan era modern, olahraga sepeda telah menjelma menjadi lebih dari sekadar aktivitas fisik. Bukan hanya...
Dalam beberapa tahun terakhir, perangkat pendingin pembersih udara mini semakin populer di kalangan masyarakat Indonesia. Alat ini...
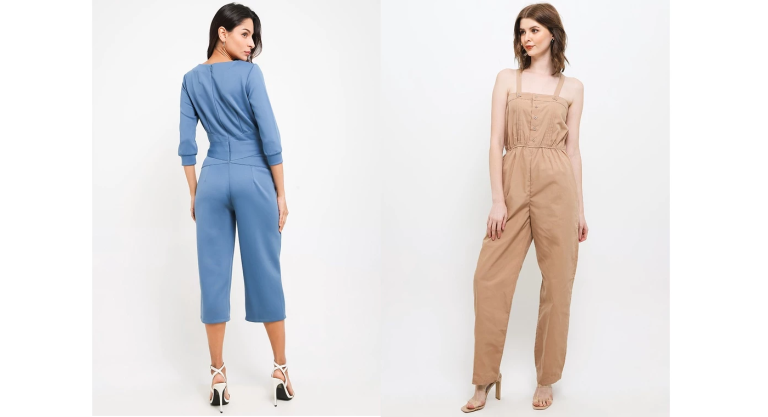
Jumpsuits dan overalls telah menjadi pilihan favorit bagi banyak orang tua yang ingin memberikan tampilan stylish sekaligus...
Tugu Biawak Wonosobo: Antara Kontroversi Anggaran dan Keindahan Realistis yang Viral di Media Sosial
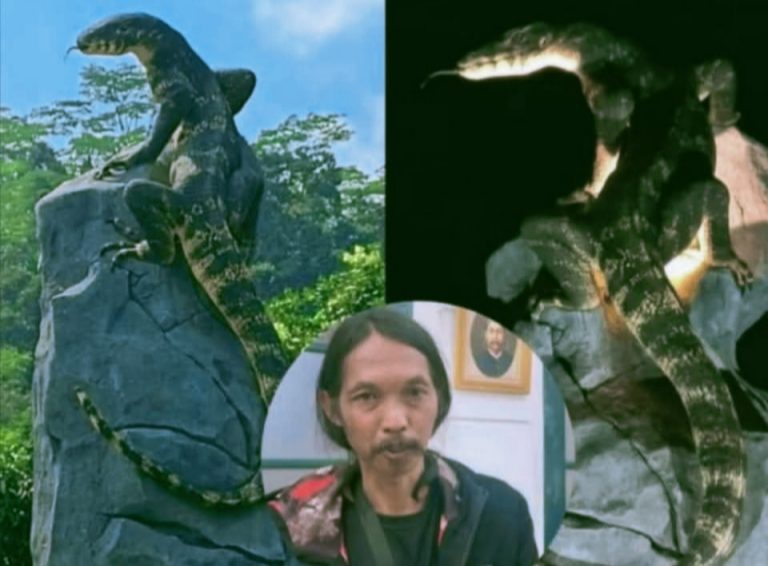


Tugu Biawak Wonosobo: Antara Kontroversi Anggaran dan Keindahan Realistis yang Viral di Media Sosial
Di era media sosial yang serba cepat, sebuah karya seni publik bisa menjadi viral dalam hitungan jam....
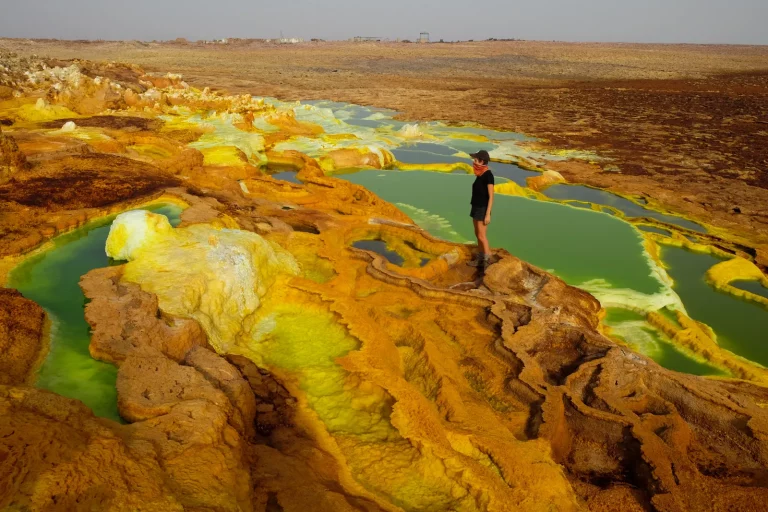
Danau Karum, sebuah danau asin yang terletak di wilayah Afar, Ethiopia, adalah salah satu keajaiban alam yang...
Di dunia seni modern, ada karya-karya yang tidak hanya memukau secara visual tetapi juga memiliki makna mendalam...
Dalam dunia bisnis yang kompetitif, efisiensi operasional adalah kunci keberhasilan. ChatGPT, teknologi AI canggih dari OpenAI, menawarkan...
ChatGPT adalah sebuah model kecerdasan buatan yang dikembangkan oleh OpenAI. Model ini dapat memahami dan merespon bahasa...
Dalam kegelapan malam atau kedalaman lautan, beberapa makhluk hidup memiliki kemampuan luar biasa untuk menghasilkan cahaya sendiri....
Inilah era digital, di mana teknologi semakin memudahkan kita dalam menghemat waktu, biaya, dan meningkatkan produktivitas. Kecerdasan...
Korupsi merupakan isu yang tak pernah absen dari perbincangan publik di Wakanda. Dalam beberapa tahun terakhir, kasus-kasus...
Apakah Anda mencari hotel murah di Bali dengan fasilitas bathub? Kami punya panduan lengkap untuk Anda. Dengan...